RECENT POSTS
- Book chapter on micro-ROS published
- Vulcanexus includes micro-ROS
- micro-ROS Humble Hawksbill release
- micro-ROS fully supports ROS 2 features
- Micro-ROS at ROS World Workshop on Execution Management
- embeddedRTPS the new experimental middleware for micro-ROS
- micro-ROS at PX4 Development Summit 2021
- Microsoft Azure RTOS integrates micro-ROS
- Renesas and eProsima Simplify Development of Professional Robotics Applications on RA MCUs with micro-ROS Development Framework
- Timeout RMW & QoS in RCLC APIs
- All posts ...
Memory Profiling of Micro XRCE-DDS
Sep 3, 2020 francesca-finocchiaro
In response to the growing interest of the community in micro-ROS, a thorough benchmarking of the most relevant figures that are key to the product adoption is in demand.
As a first step towards this direction, we recently performed a memory footprint analysis of the Micro XRCE-DDS library, the middleware underlying the micro-ROS architecture.
The Micro XRCE-DDS Client library profiling has been performed for two simple applications, one publishing and the other subscribing to topics of known size, running on FreeRTOS, chosen by virtue of its memory management capabilities, and on an Olimex STM32-E407 board, which is the reference board of the micro-ROS project. The board is connected by serial transport (UART) at 115200 baud to a Micro XRCE-DDS agent running on a Linux machine. Notice that the XRCE-DDS Client is completely dynamic memory free, so all memory figures refer to the stack and static memory usage.
The results for this analysis are summarized in the graphs below for publisher and subscriber applications, respectively.
-
Publisher Applications:
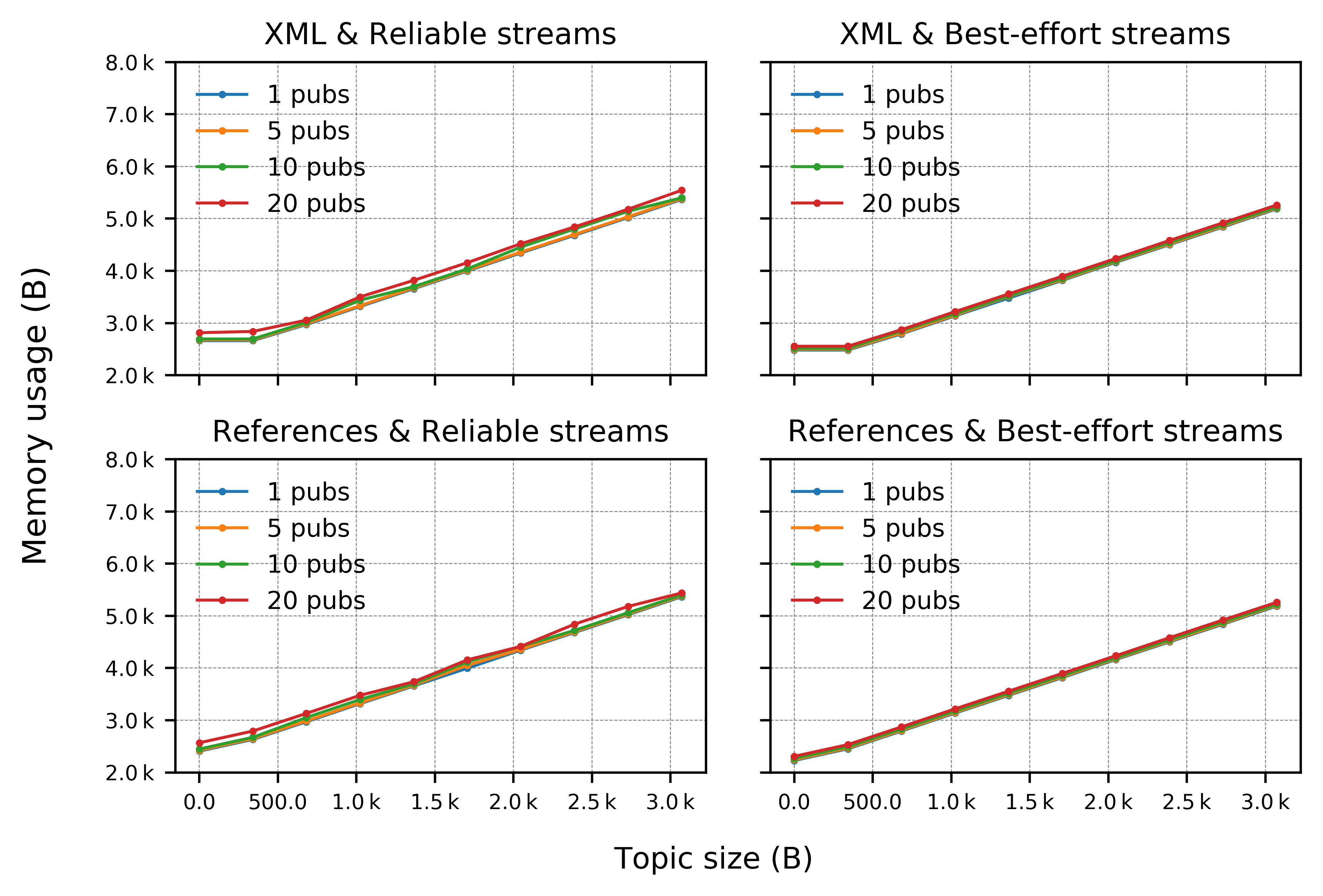
-
Subscriber Applications:
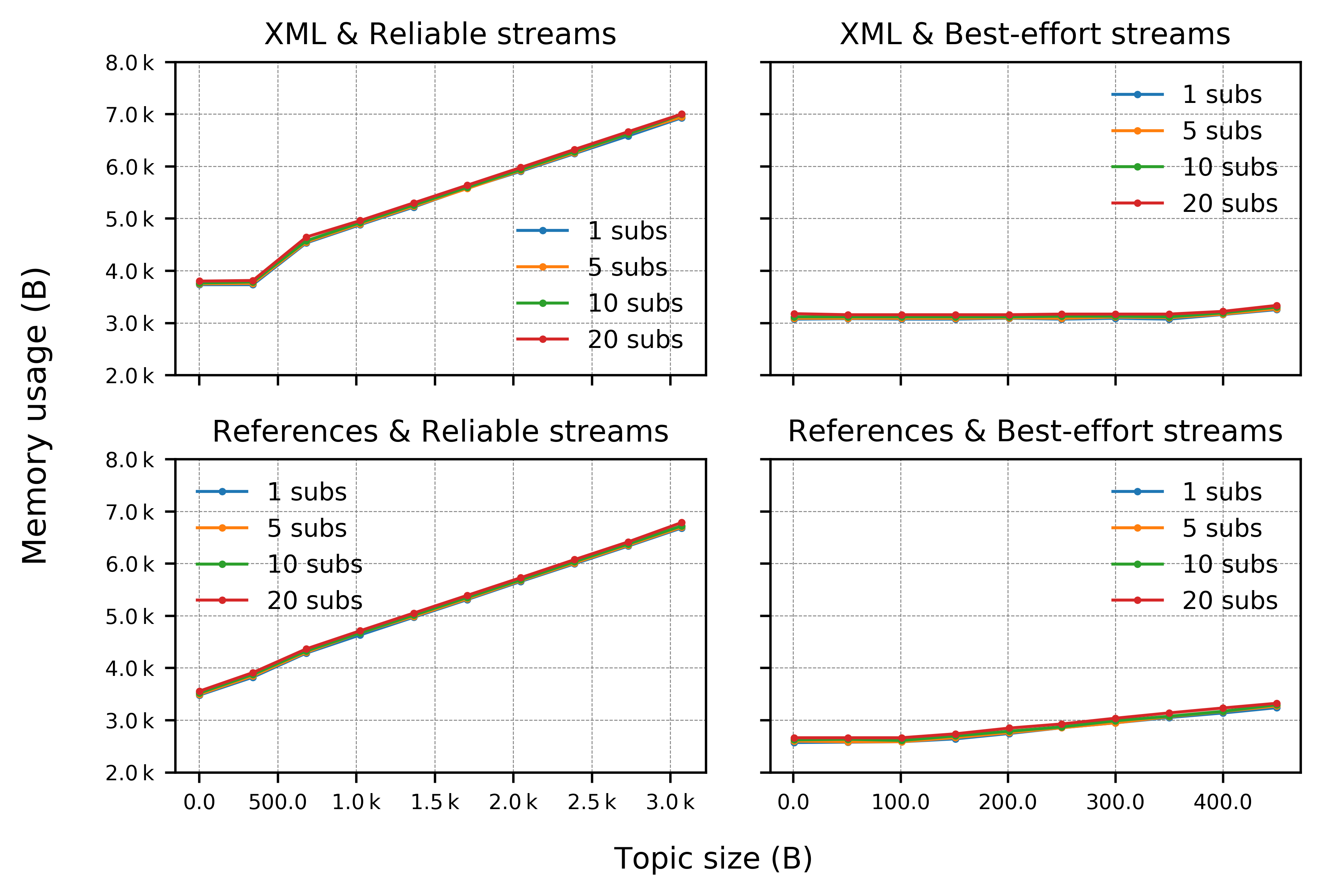
On the server side, we have investigated the memory consumption of an Agent communicating with a mock Client application on Linux that is publishing and subscribing to topics of known size, by measuring the binary size of the compiled agent (which resulted to be of 385 KB) and analysing heap and stack usages. The results for the latter are summarized in the plot below.
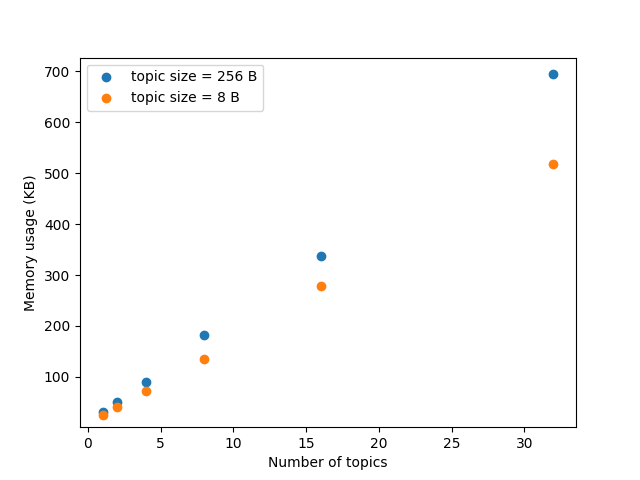
For more information regarding the methodology employed for performing these profilings, refer to the full report published on eProsima’s webpage.
Share on: